Restaking is a mechanism for reusing ETH already staked in the main Ethereum network or in liquid staking pools on other blockchains.
Users receive derivative tokens (wrapped assets) and can use them on platforms running on the EigenLayer protocol. These assets are then used to participate in securing external systems not directly related to the Ethereum virtual machine.
In the spring of 2023, the Ethereum ecosystem underwent significant changes thanks to the Shapella update. It included adjustments to the consensus protocol and, for the first time, opened up the possibility of withdrawing coins from the Beacon Chain deposit contract. Access to previously locked funds became a powerful driver of increased liquidity and gave impetus to the development of various staking options.
After Ethereum's transition to an improved Proof-of-Stake model, staking became a more convenient and secure tool for generating passive income comparable to the returns of the PoW mining era. The Shapella hard fork removed technical limitations that hindered infrastructure development and laid the foundation for the emergence of new technologies. One of the key areas that emerged as a result of these changes was restaking — a new stage in the evolution of ETH usage on the network.
Source: GoMining
The difference between staking and restaking
In classic staking, the user freezes a certain amount of coins in the network, thereby supporting its stability and validating transactions. In return, they receive a reward in the form of interest. During the lock-up period, tokens cannot be withdrawn or used, which is similar to a regular bank deposit, where funds are unavailable until the end of the deposit term.
Restaking works differently: already staked or «liquid staked» assets can be used for additional tasks. Coins or tokens derived from them can be re-included in other protocols and pools, allowing the owner to earn additional income while participating in other DeFi instruments.
At its core, the concept of restaking echoes the model of combined minting in PoW networks. There, a miner can mine several coins at once if the algorithms are compatible with each other, without sacrificing overall computing power. The same logic applies here: assets already operating in one PoS process can be used in other mechanisms without losing their main functionality.
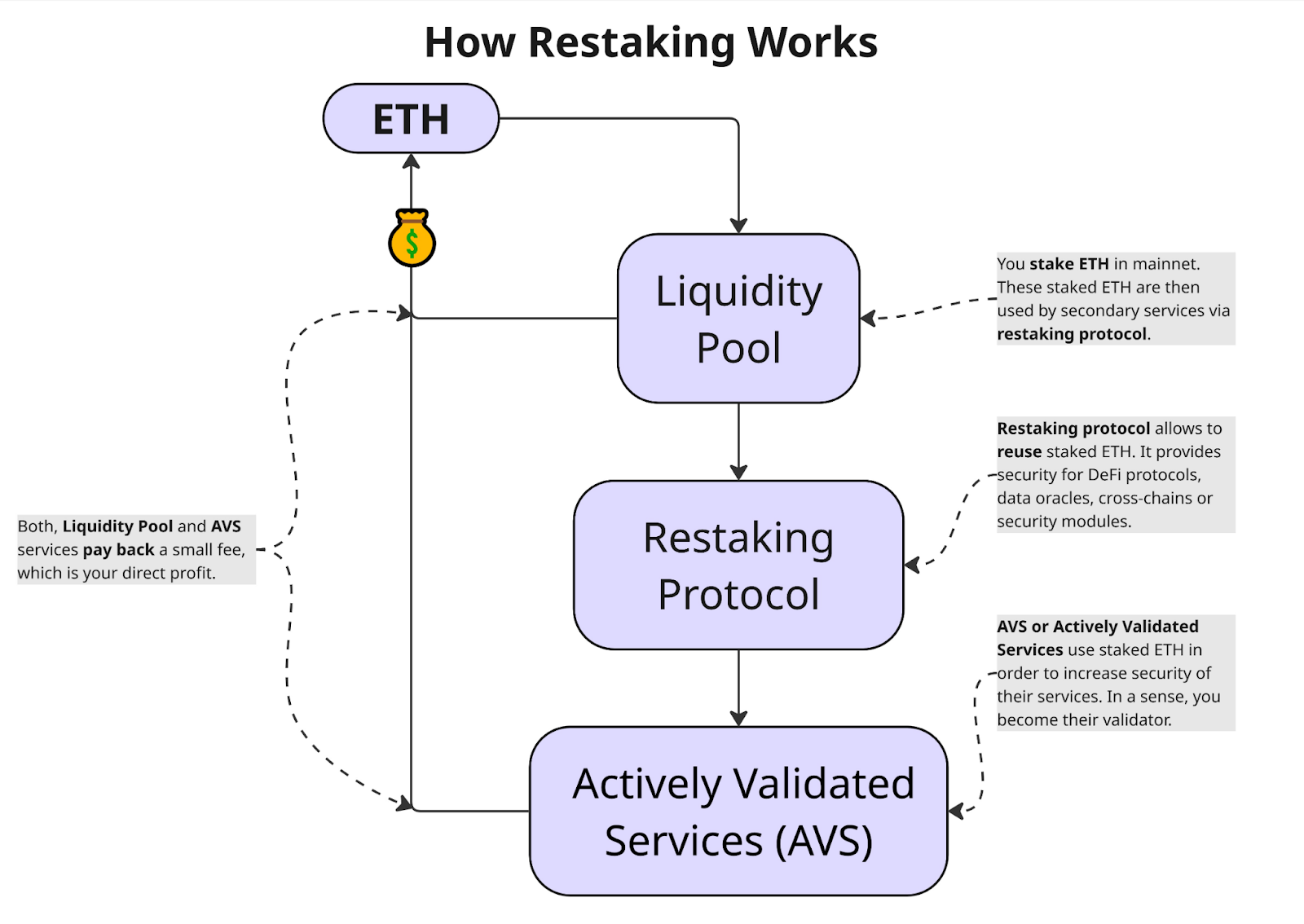
How restaking works
1. Initial asset locking. The owner of the funds first «stakes» their tokens (e.g., ETH) on the network — this can be native staking or participation in liquid staking pools (Lido and similar services). As a result, an asset appears that is tied to network validation.
2. Transfer to the restaking layer. Next, the staked assets (or their derivative tokens) are transferred to a restaking platform — for example, the EigenLayer protocol. This platform acts as a bridge between the main blockchain and external services that are ready to accept security from existing stakers.
3. Connection to additional services. The user or validator operator selects the external services to which they want to provide their protection — the so-called Actively Validated Services (AVS). These can be oracles, cross-chain bridges, security modules, and other DeFi components that need security guarantees.
4. Combining roles and risk management. When restaking, assets continue to serve as collateral for the main network, but at the same time may be responsible for the correct operation of the selected AVS. This adds new operational and economic conditions — for example, requirements for validator action snapshots and slashing conditions.
5. Additional income. For providing security to third-party protocols, the participant receives a reward in addition to the base staking yield. These bonuses accumulate together with the usual staking rewards, increasing the overall return on capital.
What is liquid restaking?
Liquid restaking is an advanced restaking model that allows users to keep their assets unlocked. In traditional restaking, tokens remain inaccessible for the entire period of participation, but in the liquid format, the system issues special derivative coins called Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRT).
Such assets include, for example, eETH, ezETH, pufETH, and other variants issued by different protocols. LRT tokens reflect the user's share in restaking, but remain fully liquid: they can be sold and bought on exchanges, used as collateral, moved between DeFi applications, or added to liquidity pools.How liquid restaking works
1. ETH deposit. You send your ETH to a liquid restaking platform (e.g., Ether.fi) to start participating in the process.
2. Receiving LRT tokens. In response, the platform issues special tokens representing your assets — Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRT), such as eETH, at a 1:1 ratio to the amount deposited.
3. Use in DeFi. These tokens can be used in other protocols, such as Uniswap, Aave, or liquidity pools, to earn additional income, while the ETH itself remains staked.
4. Accrual of rewards. You continue to receive rewards from restaking, which accumulate in your balance along with income from using LRT in DeFi.
5. Flexibility and profitability. Liquid restaking allows you to simultaneously maintain access to assets and maximize profits by combining stable income from staking with the capabilities of the DeFi ecosystem.
What is EigenLayer?
EigenLayer is an innovative protocol that adds an additional infrastructure layer to the Ethereum ecosystem. It creates a new type of cryptoeconomic security, allowing third-party projects to rely on the reliability and stability of the main network without having to build their own security model from scratch.
Thanks to EigenLayer, developers can
1. Leverage the strength and authority of Ethereum at the consensus level, using it as the foundation for their security;
2. Independently determine how to apply restaking to support their own services or networks;
3. Attract more participants by encouraging the reuse of staked assets and increasing the overall economic efficiency of the ecosystem.

Source: Еigenlayer.xyz
Is it possible to earn money through restaking?
Restaking provides users with new opportunities to earn income that may be higher than with standard staking. However, the final profit depends on several factors:
1. Market volatility. Cryptocurrencies are subject to significant price fluctuations, so it is important to monitor the market situation and consider the possible risks of losses.
2. Interest rates and rewards. The return on staking and restaking varies depending on the platform, asset type, and selected third-party services (AVS). Choosing the optimal platform with high rates allows you to maximize your profits.
3. Asset lock-up period. The longer your coins remain in the pool or participate in restaking, the higher the final income due to the compound interest effect.
4. Platform fees. Some services charge significant fees for participating in staking and restaking. It is important to assess in advance how much they reduce your potential earnings.In conclusion
Restaking is an effective tool for those who want to increase their staking returns. The ability to automate processes and use liquid restaking makes this strategy particularly attractive for both experienced investors and beginners.
As with any investment activity, when working with restaking, it is important to carefully select platforms, analyze potential risks, and make informed decisions.
For those looking for ways to earn passive income in the cryptocurrency sphere, restaking can be a convenient and promising starting strategy.
Subscribe and get access to the still free GoMining course on crypto and Bitcoin https://academy.gomining.com/courses/bitcoin-and-mining
November 27, 2025













