Automated market maker (AMM) — a software algorithm for controlling liquidity and pricing of crypto assets on decentralized exchanges.
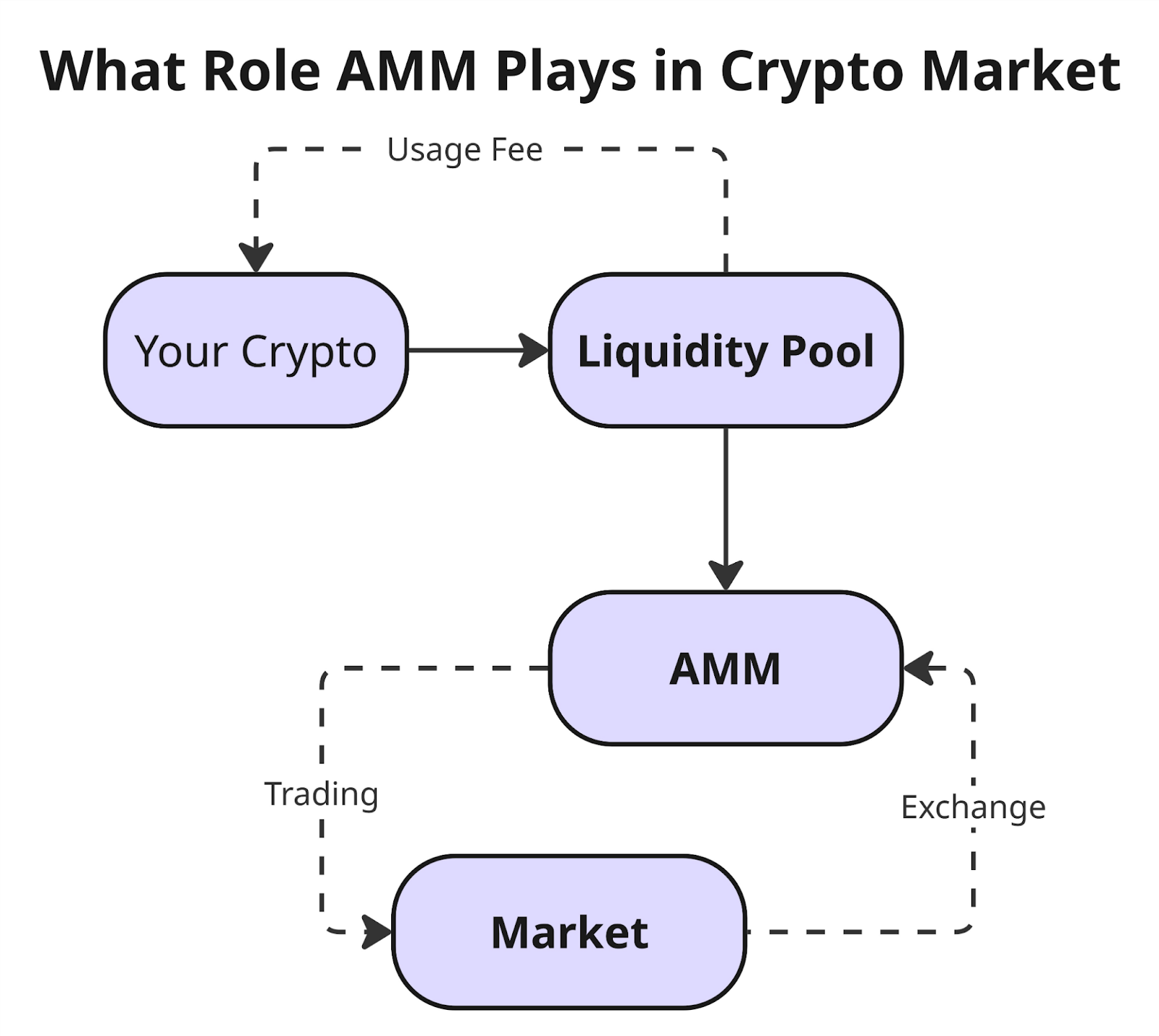
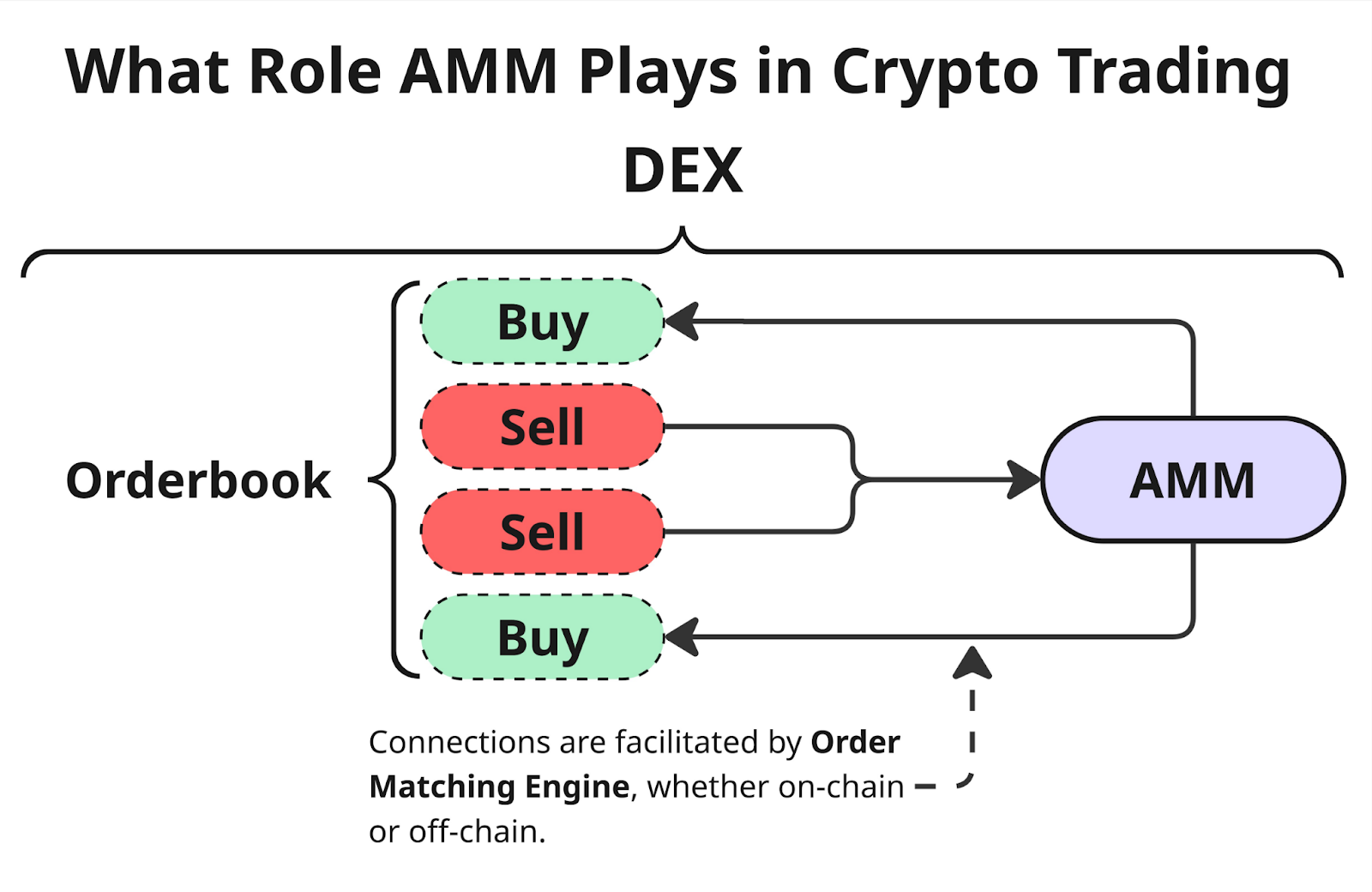
Instead of a traditional order book, AMM uses a liquidity pool — a set of tokens locked in a contract. This allows transactions to be executed automatically, with the price being determined dynamically based on the ratio of assets in the pool.
Source: GoMining
How AMM works in Crypto Exchange and Trading Market
An automated market maker operates on the basis of liquidity pools — special smart contracts into which users deposit token pairs. In exchange, they receive liquidity tokens (LP tokens) that reflect their share in the pool and entitle them to a portion of the fees.
When an exchange occurs, the AMM calculates the price based on a programmed algorithm. The most commonly used formula is the constant product (x · y = k), which automatically adjusts the value of assets depending on their current balance in the pool. This approach allows transactions to be conducted without a traditional order book and ensures continuous liquidity.
The main stages of AMM:
1. Providing liquidity. Users contribute token pairs to a liquidity pool managed by a smart contract.
2. Determining the price. The value of assets is determined algorithmically, usually based on a mathematical formula that takes into account the ratio of tokens in the pool.
3. Trading and exchange. Traders exchange assets by interacting directly with the pool. After each transaction, the balance changes and the formula automatically recalculates the price.
4. Incentives for participants. To attract liquidity providers, AMM protocols distribute a portion of transaction fees or other types of rewards among them.
Features of Cryptocurrency AMM
1. Decentralization. AMM operates without a central governing body. All transactions are conducted through smart contracts, and trading decisions are not dependent on any organization. This approach eliminates the single points of control and failure that are characteristic of centralized exchanges.
2. Use of smart contracts. Smart contracts automatically manage asset exchanges and price calculations. Transactions are executed according to a predefined formula, without the involvement of intermediaries or operators.
3. Non-custodial model. Users retain control over their funds until the exchange takes place. AMM does not hold assets and does not require the transfer of management rights to third parties.
4. Transparency of operations. All protocol actions are recorded on the blockchain. This allows you to check the transaction history and current pool balances without the possibility of hiding data.
5. Algorithmic pricing. Asset prices are determined by a formula based on the ratio of tokens in the pool. This mechanism reduces the influence of individual participants on price levels, unlike traditional order books, where the price depends on the actions of buyers and sellers.
Advantages of AMM
1. Decentralization. AMM operate without a central governing body, and all transactions are conducted through smart contracts.
2. Access to liquidity. AMM pools allow users to exchange tokens and provide funds for trading operations without intermediaries.
3. Automation and new trading models. AMMs use algorithms to calculate prices and execute transactions, creating new trading mechanisms within DeFi.
Disadvantages of AMM
1. Impermanent loss. Liquidity providers may incur losses when there are sudden changes in token prices within the pool.
2. Limitations on scalability and capital efficiency. Early AMM models require significant reserves to maintain liquidity, which can reduce capital efficiency.
3. Smart contract vulnerabilities. Errors in the code or contract vulnerabilities can lead to protocol failures and loss of participant funds.
Risks and challenges of AMM
1. Smart contract vulnerabilities. AMM relies entirely on smart contracts. Any errors in the code or vulnerabilities can lead to incorrect protocol operation, loss of participants' funds, or transaction processing failures.
2. Impact of market volatility. Prices in AMM are calculated based on the ratio of tokens in the pool. When the market changes sharply, liquidity providers (LP) may incur losses compared to holding assets outside the pool. This phenomenon is known as impermanent loss.
The role of AMM in DeFi
Source: GoMining
1. Providing liquidity. AMM. allows transactions to be carried out at any time using liquidity pools, without the need to find a counterparty.
2. Access to market creation. Any user can contribute funds to the pool and act as a liquidity provider, participating in market formation.
3. Automating token exchange. AMMs automatically calculate prices based on the ratio of tokens in the pool, which simplifies the exchange of a wide range of crypto assets in the DeFi ecosystem.
The Future of AMM
1. Integration with traditional finance. AMM models can be used in conjunction with traditional financial instruments, creating hybrid structures that combine algorithmic pricing with existing market mechanisms.
2. Technological development. Improvements in blockchain technology and smart contracts expand the capabilities of AMM, enabling more accurate price determination and transaction processing.
3. Impact of the regulatory environment. Financial market regulation defines the framework for the use of AMM and influences their implementation and integration with other financial systems.
In conclusion
Automated market makers (AMM) have changed the way trading is organized in decentralized finance, providing an alternative to the traditional order book model.
AMMs use liquidity pools and algorithms to calculate prices, allowing exchanges to take place without the involvement of a specific counterparty and maintaining market accessibility regardless of the activity of individual participants.
The growth of AMM usage in the DeFi sector shows a shift towards systems where trading is based on smart contracts and mathematical rules rather than the actions of buyers and sellers.
Subscribe and get access to the GoMining course on cryptocurrency and Bitcoin, which is still free: https://academy.gomining.com/courses/bitcoin-and-mining
January 5, 2026














