First, let's break down what a bridge is in cryptocurrency. Essentially, a bridge connects two different blockchains and allows digital assets to be transferred between them. You can think of it as a real bridge between two islands: one blockchain is one island, and the other blockchain is the second. The bridge allows assets to be moved from one island to another.
Why is this important? Blockchains operate independently of each other, so assets and data are often isolated. Bridges eliminate this isolation, enabling token transfers and interaction between different networks.
There are different types of bridges:
1. Custodial bridges. They transfer assets through a third party that stores them until the transfer is complete.
2. Decentralized bridges. They use smart contracts: they automatically conduct transactions without the involvement of an intermediary.
The security of bridges depends on how they are built. Assets are actually moved between networks, so if the protocol is not secure, they can be stolen. To prevent this, developers use multi-signature schemes and built-in transaction checks to ensure that assets cannot be taken by outsiders.
Source: GoMining.com
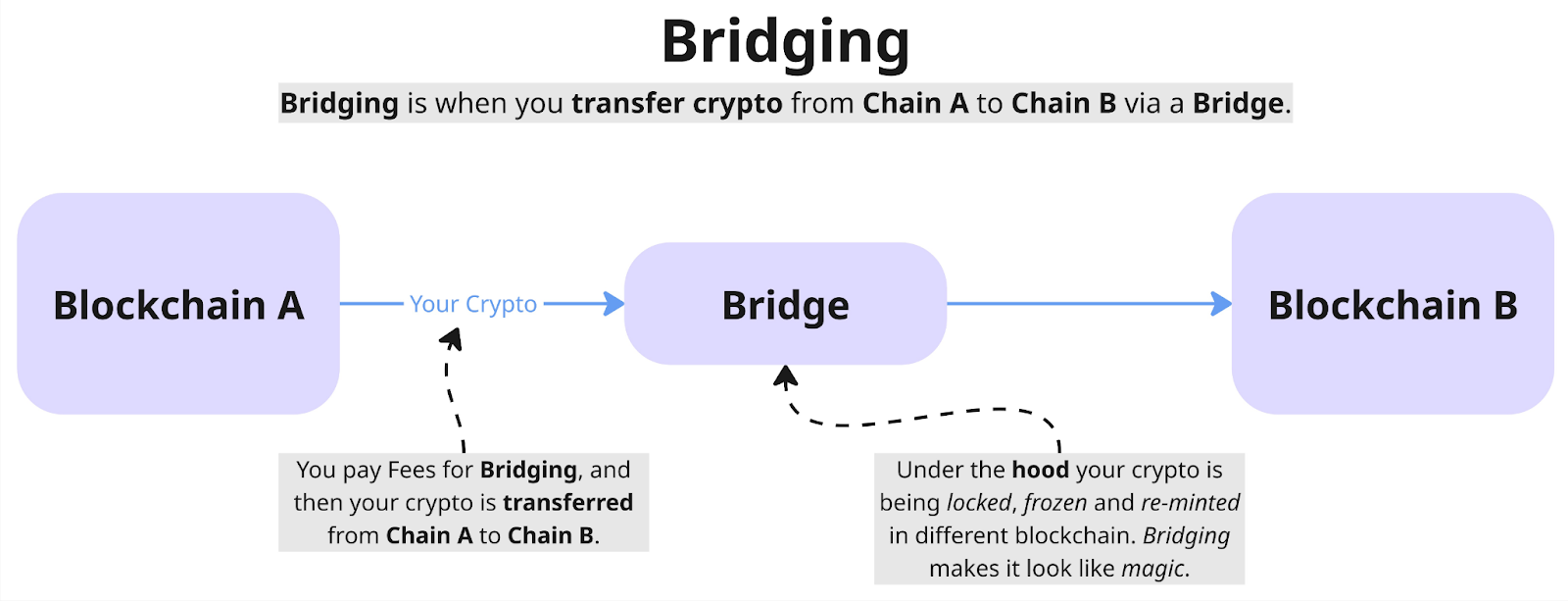
Understanding Bridging
Decentralized finance is built on ecosystems of blockchains, networks, applications, and exchange platforms. They work together for various tasks: transferring funds, purchasing goods and services, launching applications and platforms, and conducting transactions.
Each blockchain is structured differently and uses different technologies. For example, Ethereum uses a complex consensus protocol that allows the creation of tokens, decentralized applications, and games. Bitcoin mainly stores and transfers BTC using cryptography and public key infrastructure, which records transactions on the network and prevents counterfeiting.
In order for blockchains to interact with each other and with other networks, a common mechanism is needed for transferring tokens, running dApps, and verifying transactions. Since different networks are built differently, they cannot directly understand each other.
This is where crypto bridges come in. They act as intermediaries between blockchains, converting assets and data into a format that both networks understand. Cross-chain bridges allow blockchains to work together and increase the functionality of the decentralized ecosystem, making it easier for end users to interact.
Source: B2binpay.com
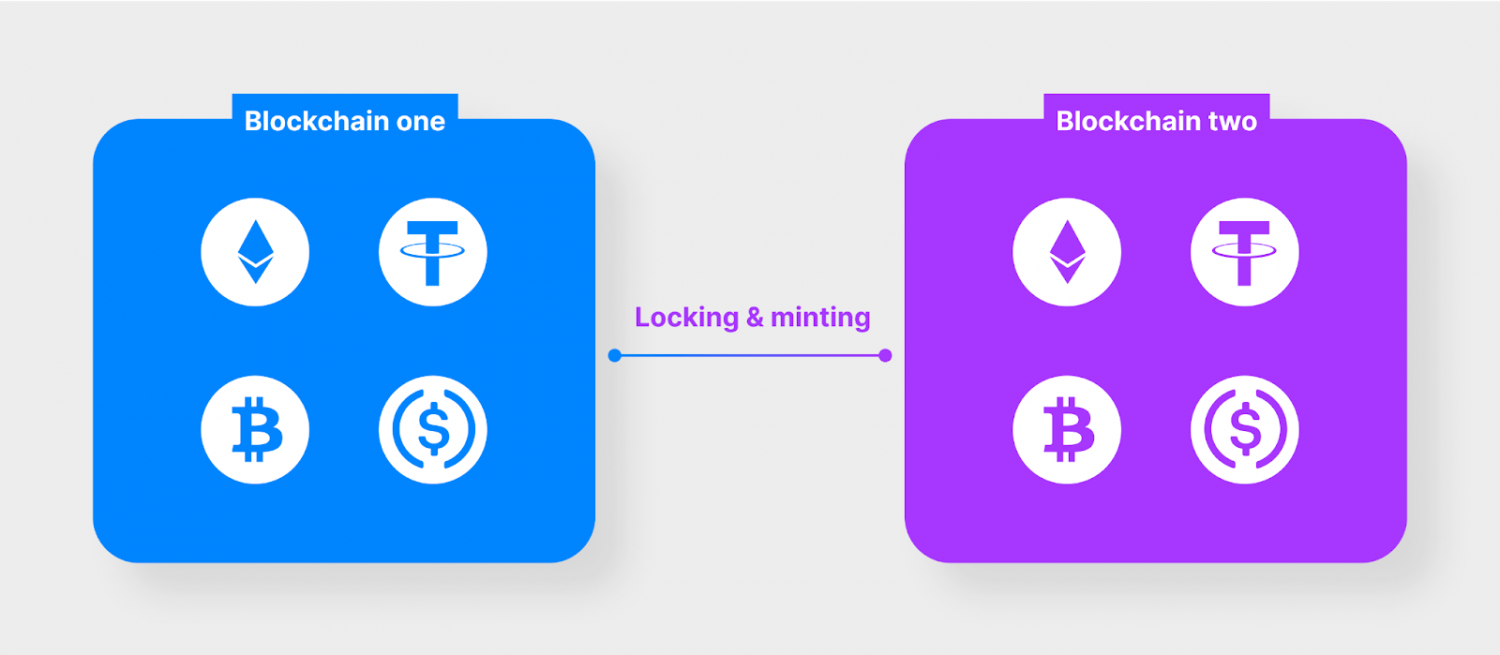
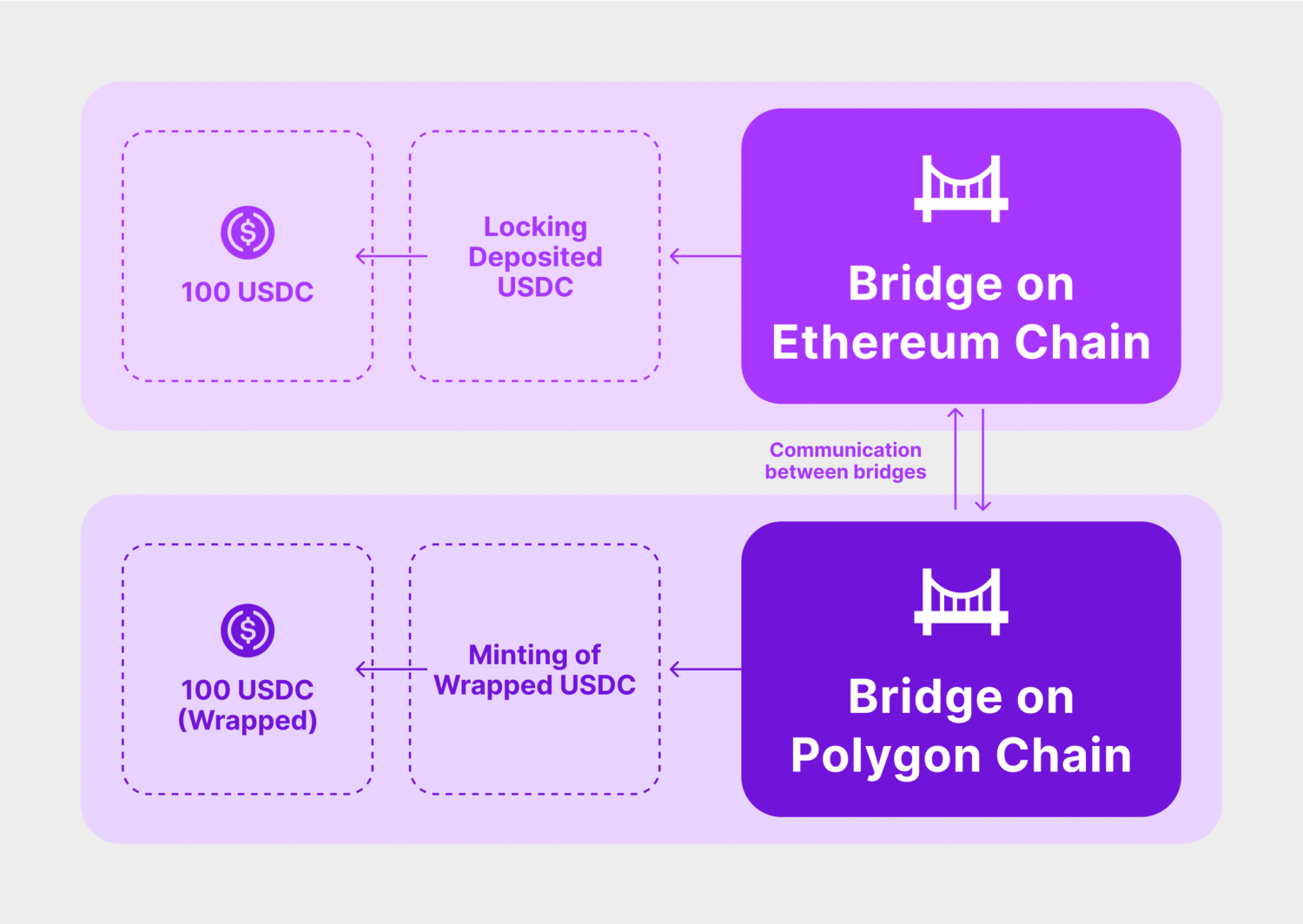
How intermediate accounts are created in cryptocurrencies
Crypto bridges work in such a way that most users do not notice their operation.
1. The user sends tokens from blockchain A, which cannot be used in blockchain B.
2. Blockchain A smart contracts block these tokens and record their status.
3. Bridge A transfers transaction information to bridge B: token type and quantity.
4. Bridge B creates new tokens in blockchain B in the same amount so that the user can use them in the new network.
Bridge transactions work both ways. If the user wants to return the tokens to the original blockchain, the new, wrapped coins are locked, and the original tokens become available again in the first network.
Source: B2binpay.com
What role do smart contracts play in transferring assets between networks?
Smart contracts are programs within a blockchain that trigger certain actions when specified conditions are met. In cross-network transfers, they take over the entire asset management process.
When a user initiates a transfer, a contract on one network locks the tokens — they become unavailable until the transaction is complete. On the other network, another contract receives a signal and releases an equivalent amount of tokens or unlocks a pre-prepared balance. Everything works according to pre-written rules, without manual intervention.
Challenges to consider when building bridges
Networks operate according to different rules: transaction formats, block confirmation methods, and data storage logic vary. Because of this, transferring assets between chains requires additional modules that convert data from one format to another.
The industry is trying several approaches: standardized protocols for data exchange between networks, improved transaction verification schemes, and solutions to increase blockchain throughput. These areas are being developed to remove technical limitations and make the transfer of assets between networks more stable in terms of mechanics.
Security issues in crypto bridging
Decentralized blockchain networks do not eliminate risks. Bridges add new points of interaction that may be vulnerable. Among the problems are errors in smart contracts, the possibility of hacking, and the risk of double spending tokens. These aspects must be taken into account when working with bridges.
Overcoming technical obstacles
Different blockchains have their own protocols and architecture, which can complicate the exchange of assets. To ensure that bridges work correctly, cross-chain interaction protocols, compatibility standards, and methods for improving scalability are being developed. These solutions help facilitate the transfer of tokens between networks and increase the efficiency of decentralized applications.
In conclusion
Different platforms build bridges in different ways: some support token compatibility, others provide liquidity or accelerate transaction processing between chains. Therefore, the choice of bridge depends on the tasks the user is trying to accomplish.
Bridges differ from crypto exchanges: they conduct transactions directly between networks and can be faster and cheaper. However, like any decentralized tool, bridges come with risks, so it is important to study how a particular platform and protocol works before using it.Subscribe and get access to the GoMining course on cryptocurrency and Bitcoin, which is still free: https://academy.gomining.com/courses/bitcoin-and-mining
January 5, 2026