A smart contract is a piece of software code that automatically executes the terms of an agreement between parties.
The code for such a contract is stored in a blockchain — a distributed database that provides a reliable and immutable record of all transactions. Once a smart contract is implemented, it independently monitors the fulfillment of agreements without the involvement of intermediaries such as banks or legal authorities. This allows for a high level of security and transparency in the automation of transactions, which is especially important when working with cryptocurrencies, ensuring reliable transactions.
The idea of smart contracts was first proposed by cryptographer and computer scientist Nick Szabo in the 1990s. He described them as a digital mechanism that allows the terms of agreements to be automatically fulfilled when certain conditions are met. In practice, the concept was realized with the advent of blockchain technology, especially after the creation of the Ethereum platform, designed to work with decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts.
Smart contracts are designed to be protected from changes and outside interference. Once placed on the blockchain, their code becomes immutable, ensuring that all conditions are executed accurately without the risk of tampering or fraud.
Source: GoMining
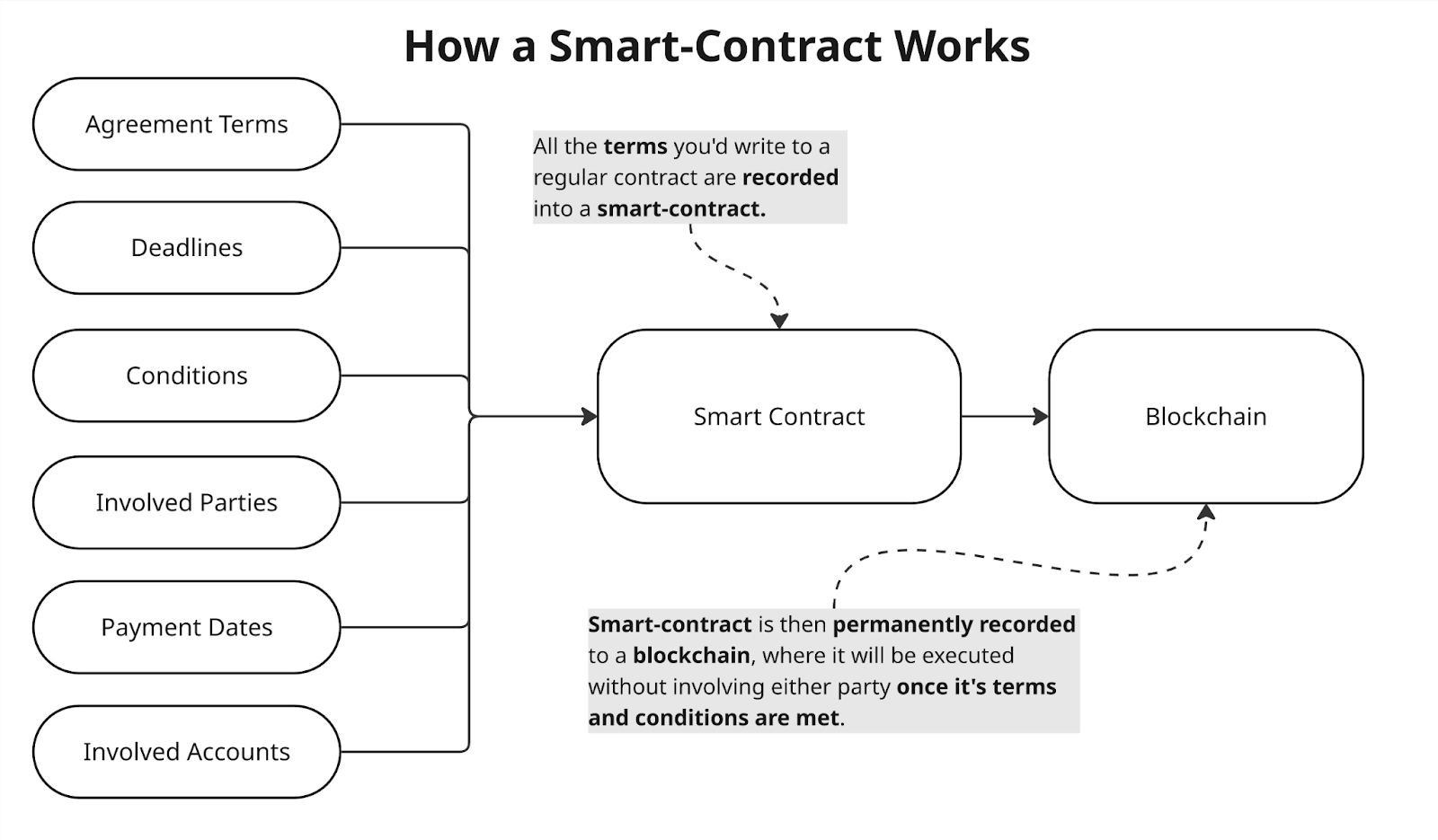
How smart contracts work
Smart contracts operate based on predefined rules that are encoded in the blockchain system. These rules, often referred to as “contract logic,” determine how the contract will respond to various events. The contract constantly monitors the blockchain for certain conditions, or «triggers». Once these triggers are activated, the smart contract automatically performs the specified actions without human intervention.For a clear example, consider a smart contract designed for a crowdfunding campaign. It may specify that if the required amount of cryptocurrency is collected by a certain date, the funds will be automatically transferred to the project author. If the goal is not achieved, the money is returned to the contributors. This approach fully automates the process and ensures transparency in the fulfillment of the terms of the agreement.
The main advantage of smart contracts is that they eliminate the need to rely on trust between the parties. The contract itself ensures compliance with all conditions, which makes it particularly valuable in cases where the parties are unfamiliar with each other or when the use of traditional legal mechanisms is too expensive or inconvenient.
How to verify a smart contract in cryptocurrency
Auditing a smart contract before launching it on the blockchain is a key step in ensuring security, reliability, and correct functioning. The main verification steps include:
1. Code verification. The audit begins with a detailed study of the contract's source code. Developers or third-party specialists analyze it line by line, identifying potential errors, vulnerabilities, and areas of code that may not work efficiently.
2. Testing. After the code is analyzed, the contract is deployed on a test network that simulates real-world conditions without the risk of losing funds. Various scenarios are created to test how the contract behaves in different situations and performs its functions correctly.
3. Security analysis. At this stage, a comprehensive check is performed for vulnerabilities, including replay attacks, integer overflow, and other common errors. Special tools, such as static analyzers, are often used to automate part of the analysis.
4. Reporting. The final stage is the preparation of a detailed report. It records the results of code verification, testing, and security analysis, and provides recommendations for correcting and improving the contract. Developers receive this report and can make the necessary changes before deploying the smart contract to the main network.
Advantages of smart contracts
1. Automation. Smart contracts independently execute the conditions specified in the code as soon as certain conditions are met. This reduces the need for human involvement, lowers the risk of errors, and makes processes more predictable.
2. Security. Contracts are protected by cryptographic methods, and their code, stored in the blockchain, cannot be changed after launch. This immutability ensures a high level of trust and protects transactions from fraud or interference.
3. Transparency. All the logic and actions of a smart contract are open on the blockchain, allowing participants to verify compliance with the terms in real time. Transparency minimizes conflicts and increases the parties' confidence in the fairness of the agreement's execution.
4. Efficiency. By eliminating intermediaries, smart contracts speed up transactions and reduce their cost. This makes them particularly useful in areas where speed and economic optimization are important, such as financial and trading systems.
Disadvantages of smart contracts
1. Complexity. Creating smart contracts requires a deep understanding of blockchain technology and knowledge of specialized programming languages such as Solidity. This makes the development process difficult for users without technical training.
2. Irreversibility. Once a smart contract is placed on the blockchain, its code cannot be changed or deleted. If errors or vulnerabilities are found in the contract, it is extremely difficult to fix them, which increases the risks of using it.
3. Scalability. As the volume of transactions on the blockchain network grows, performance may decline. Smart contracts become prone to delays and increased fees, which can limit their effectiveness under high load.
4. Legal uncertainty. The legal status of smart contracts may vary from country to country. In some jurisdictions, they may not have full legal force, which limits their applicability in official and commercial agreements.
In conclusion
A smart contract is a tool that radically changes the way agreements are executed and transactions are conducted in a blockchain environment. It ensures automatic fulfillment of conditions, increases the security and transparency of transactions, and makes processes more efficient. At the same time, such contracts have their limitations: complexity of development, irreversibility after deployment, and uncertain legal status in different countries. As blockchain technology evolves, the use of smart contracts will only expand, opening up new opportunities for innovation and transformation of traditional business processes.
Subscribe and get access to the GoMining course on cryptocurrency and Bitcoin, which is still free: https://academy.gomining.com/courses/bitcoin-and-mining
November 27, 2025












